III. C-Nitro Carbohydrates
- Page ID
- 24086
A. Group Replacement
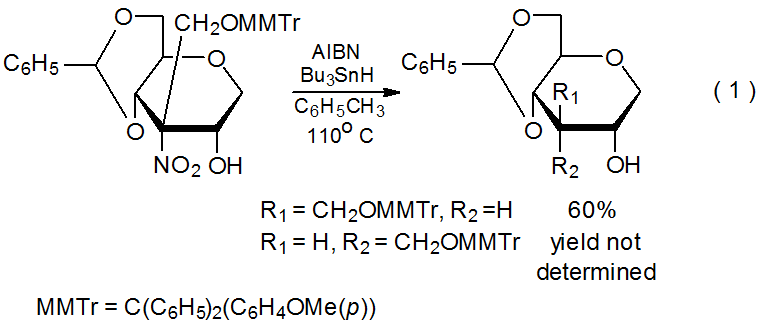
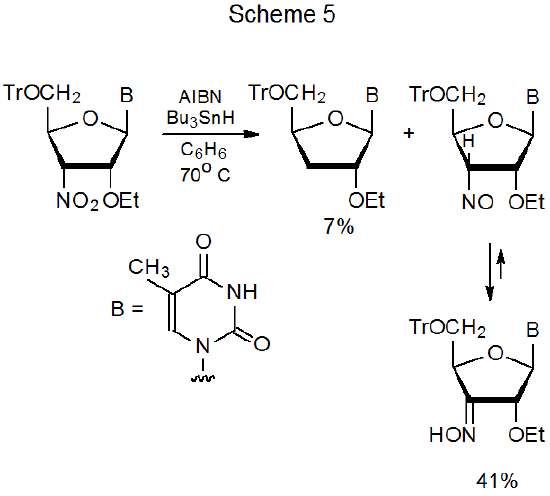
Since in the reaction of a C-nitro compound the stability of the developing radical (R·) affects the ease of cleavage of the carbon–nitrogen bond (Scheme 2), group replacement occurs more easily for tertiary nitro compounds9–14 than for secondary15–19 and, especially, primary ones.20–22 Reaction of Bu3SnH with a compound containing a tertiary nitro group is given in eq 1.9 If the nitro group in the substrate is secondary, reaction usually follows the same pathway and replaces this group with a hydrogen atom,15–18 but sometimes breaking a C–O bond leading to a nitroso compound (which isomerizes to an oxime) offers significant competition (Schemes 2 and 5).19 When a nitro group is primary, the elimination phase of the reaction is more likely to produce only the nitroso compound (eq 2),20,21 even though replacement of a primary nitro group with a hydrogen atom has been observed (eq 3).22
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=385&height=165)
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=335&height=114)
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=290&height=139)
B. Addition Reactions
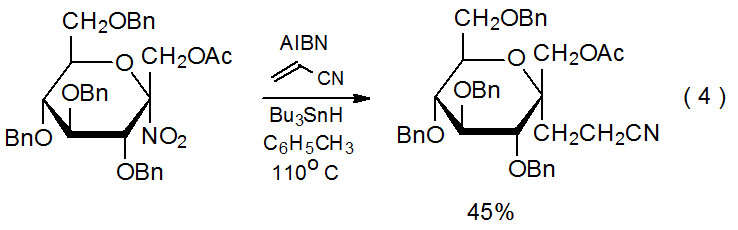
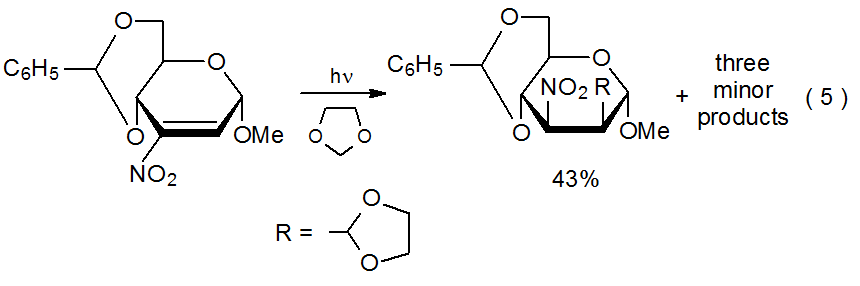
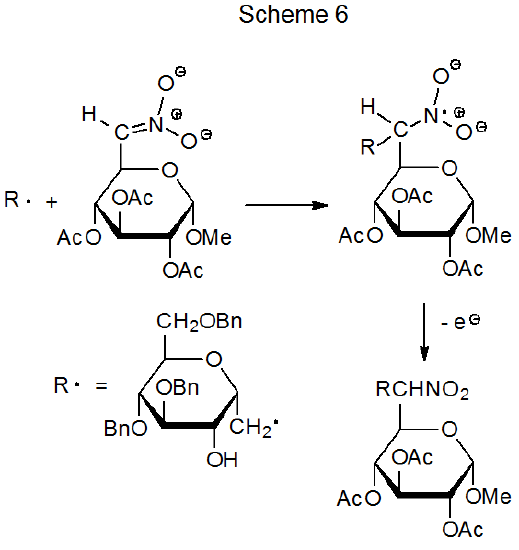
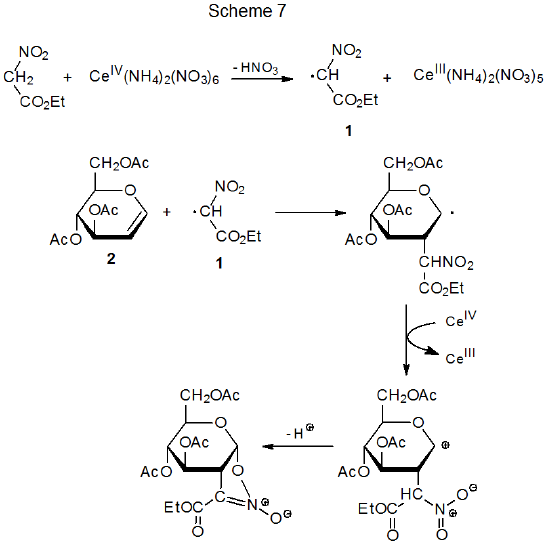
A nitro group in a reactant molecule can be involved in radical addition in several ways. First, denitration can produce a carbon-centered radical that undergoes typical addition to an electron-deficient multiple bond (eq 4).3 In a different role, nitro groups activate multiple bonds toward addition by nucleophilic radicals and affect the regioselectivity of such reactions (eq 5).23 Deprotonation of a carbon atom bearing a nitro group creates an unsaturated system to which a carbon-centered radical can add to form a new, C–C bond (Scheme 624).24–26 Finally, the electron-withdrawing character of a nitro group can contribute to turning a normally nucleophilic radical into one that is electrophilic; thus, the philicity of the radical 1, which has both nitro and ethoxycarbonyl groups attached to the radical center, is reflected in its ability to add to the electron-rich double bond in the glycal 2 (Scheme 7).27
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=370&height=115)
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=430&height=143)
C. Cyclization Reactions
A cyclization reaction that begins with a C‑nitro carbohydrate is shown in eq 6.28 The high yield of this reaction, which involves a radical centered on a tertiary carbon atom adding to a multiple bond, illustrates that radical addition can be relatively insensitive to steric congestion at the radical center.28,29
.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=300&height=203)
D. Elimination Reactions
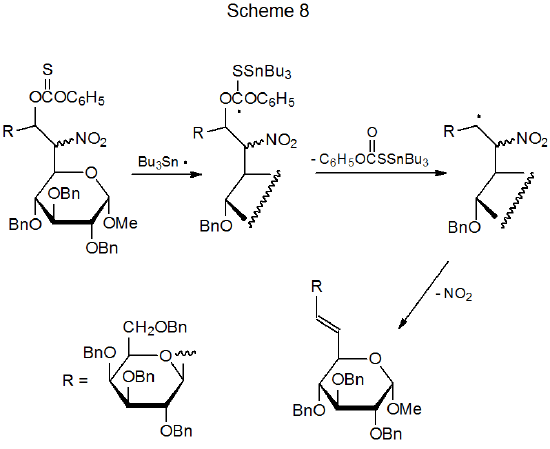
A deoxynitro sugar can undergo an elimination reaction, if a radical center develops on a carbon atom adjacent to that bearing the nitro group.30–32 In the reaction shown in Scheme 8,30 such a radical forms and then eliminates nitrogen dioxide to give an unsaturated compound.